Windows 11 has somewhat modified the appearance of the menus, already offered on Windows 8 with Settings that replace the Windows 7 Control Panel and an even greater advance on Windows 10, very close to the current Windows 11.
It’s not software that most computer users are used to opening but this tool is very useful to see the performance of the PC, prevent a program from starting on its own with Windows, access local services, etc This tutorial explains how open Windows 11 Task Manager, to access performance, processes, services and autostart applications.
The procedure is identical on Windows 11 Home or Pro, at home or at the office. The aesthetics have been slightly revised with the release of Windows 11 22H2 but the steps are identical with an older version, only the color and appearance differ a little.
If you need help with this guide or any other computer-related question, you can submit a free support request at forum Windows Facile.
Open Windows 11 Task Manager
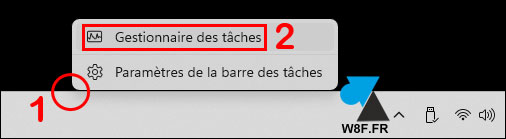
1. On the Windows 11 computer, do a right click on the taskbar (the bar at the bottom of the screen) et make a left click on « Task Manager » :
![]()
2. On the screen that opens, the menu on the left allows you to choose which information to display: click on ” Process to display the list of processes, i.e. the programs, games and utilities that are currently running on the computer. For each line, we can see the use of hardware resources: processor, random access memory, disk, network (Ethernet, Wifi), power consumption et video card.
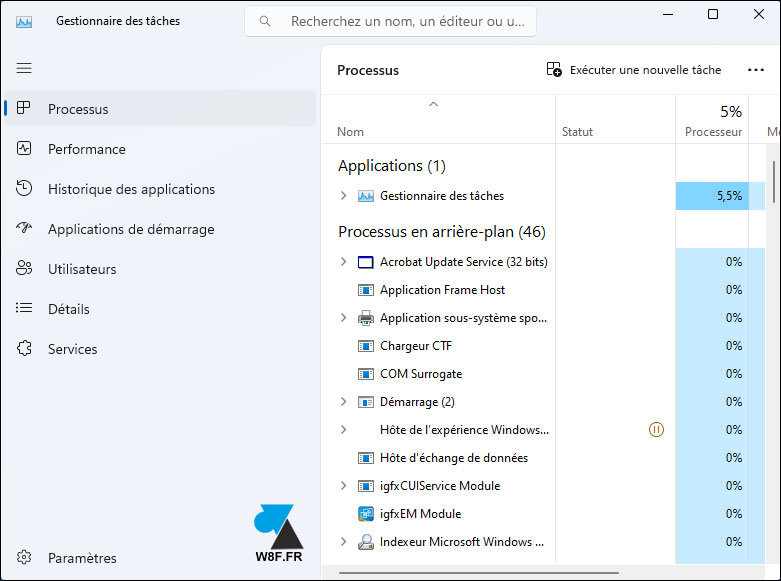
3. A click on ” Performances » displays the graphical history of the use of the processorfrom memory (RAM), discs (SSD and hard disk), connections network used (Ethernet, WiFi, Bluetooth) and GPU (graphics card processor).
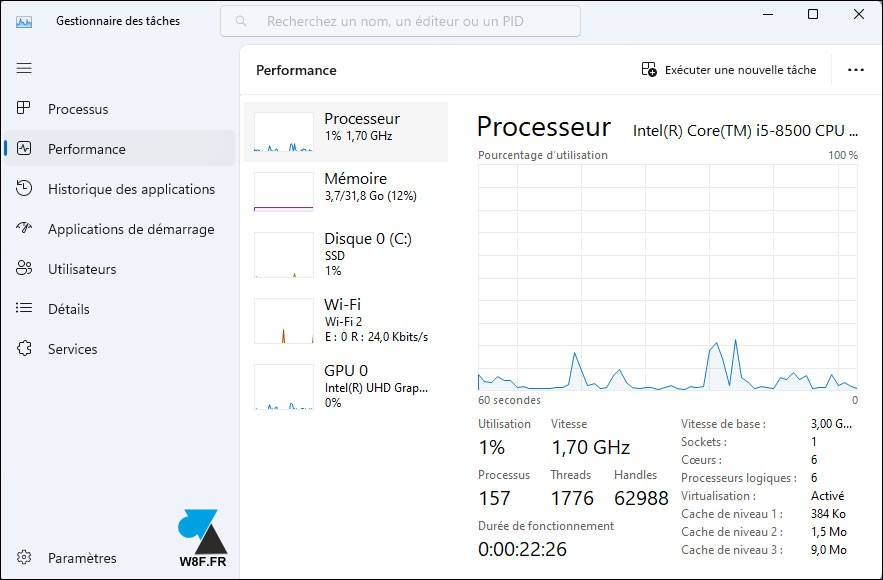
4. The menu « Starter apps » allows you to see which software and games start automatically with Windows 11. It is on this screen that you can « deactivate » the lines which should not start systematically with the computer (Steam, Dropbox, Teams, software a printer…).
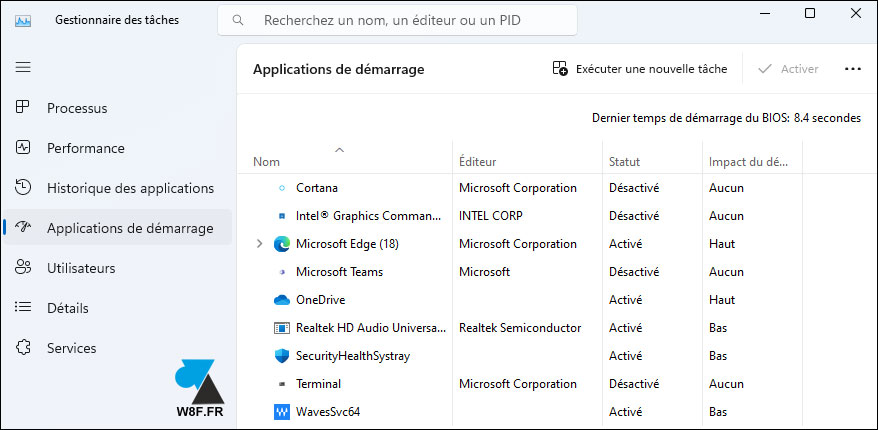
5. The menu « Services displays the list of local Windows services, that is to say everything that runs in the background, without necessarily having an icon on the desktop or in the taskbar. It is not recommended to modify elements of this long list if you do not know exactly what you want to do.
see others Windows Task Manager tutorials.

Leave a Comment